back to 44 a. - Back to content
45 a. Submedian anterior spines present and exceptionally long.
Posterior spines very long. Size 200-400 μm.Affected
negatively by bloom of green algae Botryococcus braunii
blooms in Paoay Lake (Papa et al., 2007a, 2008d).
Planktonic in lakes, and epiphytic on floating leaves.
- Laguna de Bay, Pasig River, Paoay Lake, Sampaloc Lake,
Lake Mainit.
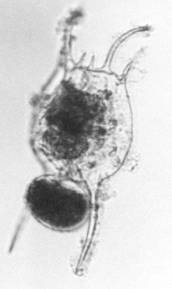
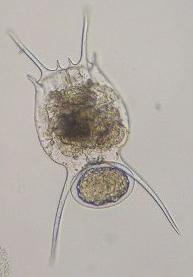
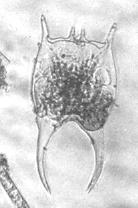
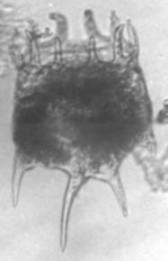
Brachionus falcatus ZACHARIAS 1898.
[1941a, 1973, 1980, 1984a, 2001a, 2008b+d, 2009a, 2011a+b+c]
B. falcatus from Laguna de Bay
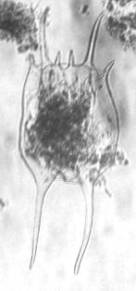
B. falcatus from Sampaloc lake
B. falcatus
(Foto: Rey Donne S. Papa)
45 b. Submedian anterior spines absent (45b-1) or short (45b-2)...................46
45 b-1. Submedian anterior spines absent...................................46a + 46b
46 a. Submedian anterior spines absent. Lateral anterior spines well
developed. Spines at the foot opening very large, thick and
bent inwards. Lorica with more or less marked ridges and dots.
Size 200-250 μm. Very polymorphic.
In sub- and tropical lakes in Africa and Asia.
- Laguna de Bay, Pasig River, Paoay Lake, Bunot Lake,
Calibato Lake, Sampaloc Lake, Tadlac Lake, Taal Lake,
Naujan Lake, Lake Lanao.
Brachionus forficula (WIERZEJSKI, 1891).
[1941a, 1980, 1984a, 2001a, 2008b, 2009a, 2011a+b+c]
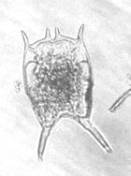
B. forficula from Laguna de Bay
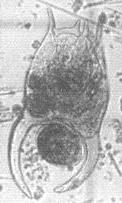
B. forficula from Laguna de Bay
B. forficula from Paoay Lake
46 b. Submedian anterior spines absent. Anterior lateral spines
thin and elongated. Lorica large, flattened and smooth.
Posterior spines usually unequal of length (f. homoceros
with spines of equal length). Body length is 200 - 550 µm,
body width is 150 200 µm. Indicator of mesotrophic
waters (Sládeček (1983) and is eurythermic = Adaptable
to a wide range of temperatures (Segers 2001b).
- Candaba Swamp (Pampanga), Taal Lake (Luzon)Brachionus diversicornis (DADAY,1883)
[1988, 2001a+b+c]
45 b-2. Submedian anterior spines short..........................46c + 46d
46 c. Submedian anterior spines short. Lateral and median anterior
dorsal spines of lorica longest. Submedian spines are rarely
present, but reduced. Posterior spines very long, usually
bent backwards. Body length is 135 - 350 µm, body width is
73 - 118 µm. This endemic american species is probably
spread from USA (type species from Illinios River, Havana, USA)
to Vietnam and the Philippines in connection with military
transport activites during the Vietnam war (Segers, 2001c).
Subic Harbor & Clark Air base?
- Laguna de Bay and nearby localities, Taal Lake.
Brachionus havanaensis, ROUSSELET, 1911.
[2001a+c, 2011a+b+c, 2012a]
B. havanaensis. Photo by Rey Donne S. Papa
46 d. Submedian anterior spines short. Lateral anterior spines small
(or absent: dwarfform, 44 a.).
Spines at the foot opening present (or absent: dwarf-form, 44 a.)
and of varying length, diverging. Highly polymorphic.
Size 100-250 μm. Planktonic in lakes.
- Laguna de Bay, Pasig River.
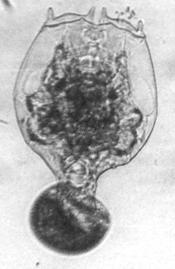
Brachionus caudatus, (BARRIOS & DADAY, 1894)
[1941a, 1978a+b, 1980, 1984a, 1986a, 2009a, 2012a]
B. caudatus from Laguna de Bay
B. caudatus - dwarf-form (44 a.):
A dwarf is a mature individual that is smaller than usual
for the species. A critical length, 115 μm has to be reached
before spines develop to any extent on B. caudatus, (Green 1960).
Some factors leading to dwarfing in tropical crater lakes
(Africa) is high temperature, low ratio of drainage area
to surface area of the body, low food supply, including
Microcystis-bloom, high salinity, and size selective
predation from cyclopoid copepods. B. caudatus produce
successfully dwarfs more readily than other species
of Brachionus.
B. caudatus dwarf form
from Laguna de Bay
(Photo: Rey Donne S. Papa, 2007)PLATIONUS, Segers, Murugan and Dumont, 1993
Brachionus-like. Foot long, with 3 sections.
Lorica granulated, with 6 anterior spines.47 a. Ventral anterior margin of lorica with strong spines.
Size 150-250 μm Mostly benthic. In ponds and lakes.
A common member of the planktonic community.
As a basal member of the food web, it plays an
important role in nutrient cycling and provides food
for higher trophic levels. 150-250 μm.
Cosmopolite, thermophilic(Arora and Mehra 2003a).
Plationus patulus was removed (Segers et. al 1993)
from the genus Brachionus based on morphological
characters of trophi.
- Laguna de Bay, Paoay Lake, Lake Lanao, Lake Leonard,
IRRI rice field
Plationus patulus (O. F. MÜLLER, 1786)
(syn. Brachionus patulus.)
(syn. Platyias patulus)
[1941a, 1978a+b 1980, 1984a, 1986, 1999]