32 a. Lorica present, i.e. cuticle thickened to form a
stiff shell (lorica), which retain its shape well after
preservation..........................................................33
32 b. Lorica absent, i.e. cuticle thin and flexible, not usually
retaining its shape well after preservation. Rather big
viviparous rotifers...................................................34
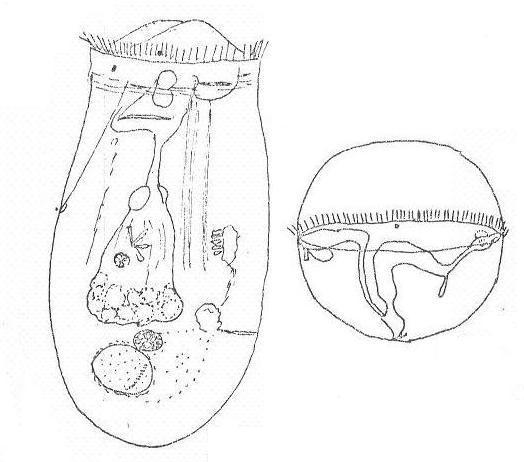
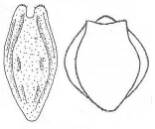
33 a. Lorica oval to boat-shaped, with fold down the sides where dorsal
and ventral plates meet. Tear-drop-shaped eggs attached to egg
carrier. Planktonic.
Anuraeopsis.....................................................52
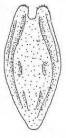
33 b. Lorica oval, 4 loped in cross section. Planktonic.
Pompholyx.......................................................69
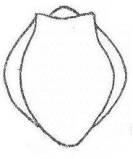
33 c. Small sack-shaped, with 4 dark masses. Yellow-green colored.
Ascomorpha......................................................63
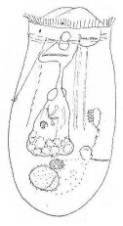
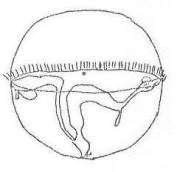
34 a. Large sack-shaped, with corona (wheel organ) anteriorly.
Intestine and anus absent. Planktonic.Asplanchna......................................................65
34 b. Large, spherical, with corona (wheel organ) in equator of body.
Trochosphaera...................................................70
Tabel 1. The genera in this key ordered after habitat
(after Ruttner-Kolisko, 1972.)
Genera with some planktonic or semi-planktonic menbers
Littoral or periphytic (or epibiontic) genera, sometimes collected in plankton
Littoreal, periphytic or benthic genera rarely or never in plankton
Brachionidae
Brachionus Keratella Anuraeopsis
PlationusPlatyias
Brachionus rubens
Euchlanidae
Euchlanis Dipleuchlanis
Tripleuchlanis
Mytlinidae
Mytilina
Trichotriidae
Trichotria
Colurellidae
Colurella
Lepadella
Lecanidae
Lecane
Trichocercidae
Trichocerca
Gastropodidae
Ascomorpha
Asplanchnidae
Asplanchnopus
Asplanchna
Synchaetidae
Polyarthra
Testudinellidae
Testudinella
Pompholyx
Trochosphaera
Filiniidae
Filinia,
(Tetramastix)
Hexarthridae
Hexarthra
Conochilidae
Conochilus,
(Conochiloides)
Collothecidae
Collotheca
to 35 a.